
Ever since 2018, the European GDPR legislation has caused companies to be more aware than ever of their responsibilities relating to the storage and management of personal information. GDPR requires businesses to ensure that personally identifiable information (PII) is protected, and one of the key strategies for achieving compliance is pseudonymization.
Unlike data anonymization, where sensitive information is removed, pseudonymization allows for re-identification by replacing identifiable information with pseudonyms or artificial identifiers. In this blog, we will define anonymization and pseudonymization, explain their difference, and discuss how automatic pseudonymization can help your company be GDPR compliant.
Let’s get started!
What is Data Pseudonymization?
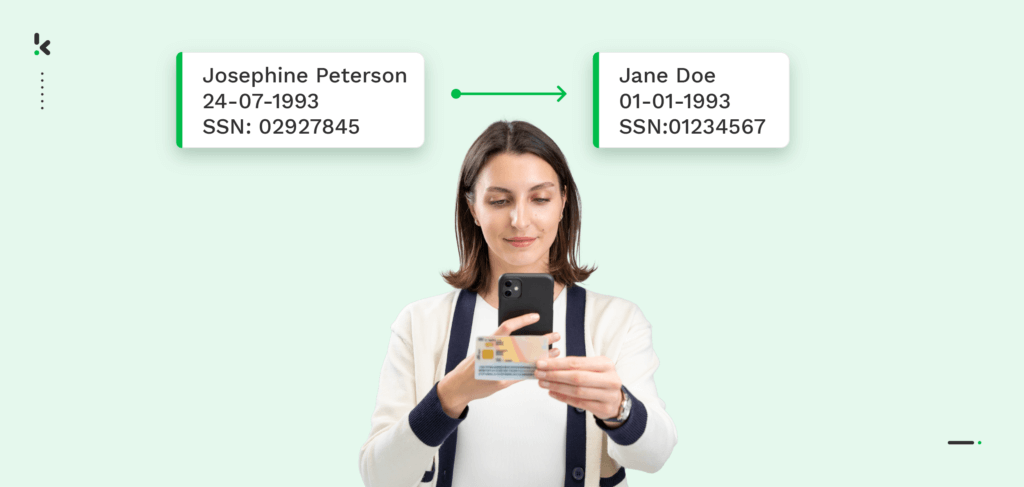
Data pseudonymization is the process of removing sensitive information, such as names or emails and replacing them with pseudonyms, aliases, or placeholder values.
Pseudonyms are described as fake names, used to conceal someone’s identity. For example, many authors use a pseudonym or pen name to cover their identity. It is important to mention that personal information, such as email addresses, location, IDs, and not just names, can be pseudonymized.
This process is reversible, meaning that concealed data can later be re-identified if necessary. Pseudonymization serves two purposes: enhancing data protection and privacy while allowing companies to use the data for legitimate purposes.
How Does Pseudonymization Work?
As we’ve seen, pseudonymization works by replacing personal information with fake identifiers or pseudonyms, making it impossible to link the data to a specific person without additional information. The link between pseudonyms and the original data is stored separately in a secure environment, often safeguarded with encryption.
The steps involved in pseudonymizing data typically include:
- Identification: Find the personal information that needs to be protected.
- Replacement: Swap the personal info with fake identifiers.
- Secure Storage: Securely store the link between the fake identifiers and the original data.
- Data Usage: Use pseudonymized data for business purposes without exposing personal information.


This process allows businesses to continue using data for analysis or processing without directly exposing personal identities.
Now that we’ve covered pseudonymization, let’s take a closer look at how it compares to anonymization. Both are designed to protect personal data, but they do so in different ways. Understanding these differences will help you choose the best solution for your needs.
Pseudonymization vs Anonymization
Pseudonymization and anonymization are two essential methods for protecting personal data, but they differ significantly in their approach and outcomes.
As mentioned, pseudonymization replaces identifiable information with a value that can’t directly identify an individual. However, this process can be reversed if necessary, which makes its privacy protection level moderate. On the other hand, with data anonymization the process of concealing sensitive information is irreversible, making the process offer the highest level of privacy protection.
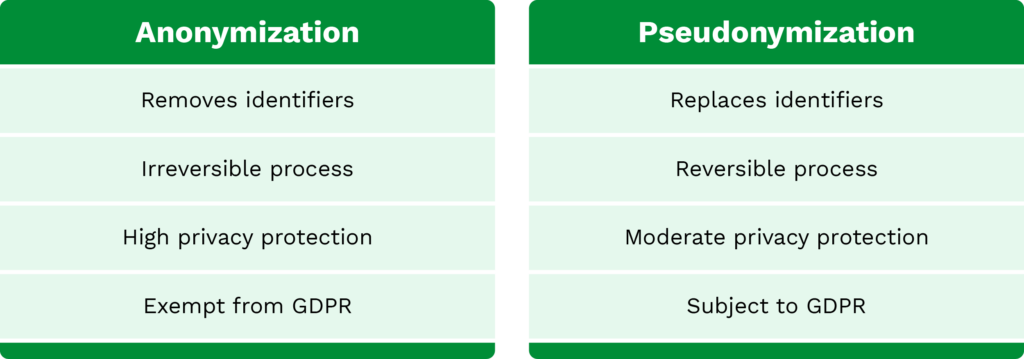

When it comes to data utility there’s a key difference. Unlike pseudonymization, anonymization removes identifiers, which makes the data much less useful. Pseudonymized data can still be used for analysis and processing, while protected, offering a balance between privacy and data utility.
While data anonymization is ideal for statistical analysis, research, and sharing data without data privacy concerns, such as public health studies. In contrast, data pseudonymization is more suitable for situations where data needs to be shared but some level of identification is still necessary for analysis or processing, like in clinical trials.
Regarding GDPR, anonymization is exempt as it no longer involves personal data. However, in document pseudonymization, the concealed data can be re-identified, meaning it is still considered personal data and subject to GDPR.
Benefits of Data Pseudonymization
Now that we’ve clarified the distinction between pseudonymization and anonymization, let’s take a closer look at the key benefits pseudonymization offers.
Improved Data Privacy
Pseudonymizing data reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by replacing identifiable information with pseudonyms, improving data privacy.
Regulatory Compliance
By using the pseudonymization technique, companies can comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR easier, avoiding legal and financial fines.
Safe Data Sharing
With pseudonymization, it’s easier to share sensitive data across organizations, departments, or third parties. This technique not only allows collaboration but also helps companies comply with data privacy regulations, without comprising individual privacy.
Preserved Data Utility
Since pseudonymization isn’t an irreversible action, it means that pseudonymized data retain their functionality and can be used in several use cases such as customer engagement campaigns, analytics research, and more, while protecting individual identities.
Lower Risk of Data Risk
In case of a data breach, pseudonymization makes it harder for the attacker to identify and access sensitive information.
Increased Customer Trust
Nowadays, customers expect companies to take care of their sensitive information. Pseudonymization helps companies demonstrate this, leading to enhanced customer trust.
Disadvantages of Data Pseudonymization
Even though there are more advantages to pseudonymization, there are still some drawbacks that need to be mentioned. Here’s a closer look at them:
Reversibility Risk
Pseudonymization is a reversible process, meaning that if additional information is available the pseudonymized data can be accessed.
Compliance Issue
While pseudonymization complies with the GDPR to a certain extent, it doesn’t fully meet GDPR requirements, as pseudonymized data may still be treated as personal information.
Implementation Complexity
Pseudonymization is a complex process requiring advanced and sophisticated software to ensure secure and efficient data handling.
Accuracy Reduction
When replacing personal identifiers with pseudonyms, some information may be lost or altered. This leads to inaccuracy when data is used for analysis or decision-making.
Understanding pseudonymization’s benefits and challenges will help protect your sensitive data better. Next, let’s explore some real-world use cases where pseudonymization can be applied.
Use cases of Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization is a powerful tool for many companies that seek to maintain a balance between utilizing data and protecting individual privacy. From healthcare and financial services to software development and research, pseudonymization is here to make your life easier. Let’s dive into its most common use cases:
Financial Services
Account numbers and credit card details can be pseudonymized while still being useful for processing and analysis. Banks and financial institutions can do that while protecting sensitive customer information.
Healthcare Research
Pseudonymized data can be shared by medical institutions to researchers, enabling large-scale studies and improving patient outcomes while protecting individual privacy.
Software Development and Testing
Real data can be used in testing environments by development teams to work with realistic information while protecting individual privacy.
Cybersecurity
Pseudonyms can replace real user identifiers to better analyze system performance, track user reputation, protect identities during security investigations, and more.
Automating Data Pseudonymization with Software
Document pseudonymization can be automated with software to streamline the process and improve efficiency. Automation offers key advantages: it ensures sensitive data is quickly and accurately replaced with pseudonyms, minimizing the risk of human error.
Automating the document pseudonymization process with the right software helps businesses enhance data security without relying on manual processes, which are prone to mistakes. It also enables companies to handle large volumes of data efficiently while maintaining privacy standards and ensuring GDPR compliance.
Most importantly, automating the pseudonymization process saves time, allowing teams to focus on core tasks and boosting overall productivity, which contributes to long-term success.
Before moving forward, you should ask yourself: Is pseudonymization “enough” to meet your needs, or is there a more secure approach to protect sensitive data?
How Can Klippa Help Securing Your Data?
If pseudonymizing data doesn’t fully cover your needs, because it can still be re-identified or doesn’t offer the complete irreversibility you need, then anonymization might be the ideal solution for your company. In any case, Klippa is here to help you implement the best data protection strategy.
If you need to anonymize data from documents, Klippa’s anonymization software can easily blackline and mask specific fields and text. Documents can be submitted via email, web, or mobile applications in formats like JPG, PNG, or PDF. After the data is anonymized, you’ll receive the processed files in your preferred format, such as JSON, XLSX, XML, or CSV.
With Klippa DocHorizon, you get the following benefits:
- Maintain data usability while automatically anonymizing sensitive information.
- Enhance compliance with privacy regulations effortlessly.
- Reduce costs by consolidating your data anonymization processes into a single solution.
- Faster turnaround times for data anonymization and processing through automation.
- Achieve seamless scalability with minimal manual intervention.
Ready to automate your anonymization process? Book a free demo via the link below or reach out to our experts for more information.
Conclusion
Nowadays, compliance with GDPR, data protection, and enhanced privacy are obligatory to run a business. Companies that take a proactive approach to data privacy, will be better prepared to handle new challenges and stay ahead of the competition. So, the real question is: is your company ready to take the lead in data protection?