
Data from The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) show that consumers reported losing more than $10 billion to fraud in 2023, marking a 14% increase over reported losses in 2022. It’s the first time that fraud losses reached the benchmark of $10 billion.
With cybercriminals getting more sophisticated, traditional authentication methods such as passwords and PINs are no longer sufficient to protect our sensitive data. The need for more secure, reliable, and convenient authentication methods has led to the development of biometric authentication.
But what exactly is biometric authentication, and how does it work?
In this post, we’ll explore biometric authentication methods like facial recognition, liveness checks, and fingerprints, highlighting their pros, cons, and applications.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that uses unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voice, to verify a person’s identity. It offers a more secure and convenient alternative to traditional methods like passwords, as biometric traits are difficult to replicate or steal.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
Biometric authentication works by capturing and analyzing unique physical characteristics to verify a person’s identity. Here’s a simplified process:
- Enrollment: The system records your biometric data (e.g. fingerprint, face, iris, or voice) and creates a template, which is a digital representation of your unique biometrical features.
- Capture: When you attempt to authenticate, the system captures your biometric data again (e.g. scanning your fingerprint or face).
- Comparison: The captured data is compared to the stored template. If there’s a match, you’re granted access (e.g. to your account, or the building you want to enter).
- Decision: If the match meets the system’s threshold for accuracy, you’re authenticated; otherwise, access is denied.
The technology behind biometric authentication involves advanced algorithms and machine learning. These systems are trained to recognize unique patterns and characteristics within the biometric samples provided by users.
Over time, the system becomes more accurate as it is exposed to a larger number of biometric samples, making it increasingly difficult for fraudsters to impersonate users. As a result, biometric authentication has become one of the most secure and convenient methods for verifying an individual’s identity.
Let’s have a look at the most common biometric authentication methods.
6 Popular Biometric Authentication Methods
There are several biometric authentication methods available, which differ in their level of security and the type of technology used to acquire data.
The most commonly used biometric authentication methods are listed below:
1. Facial Recognition
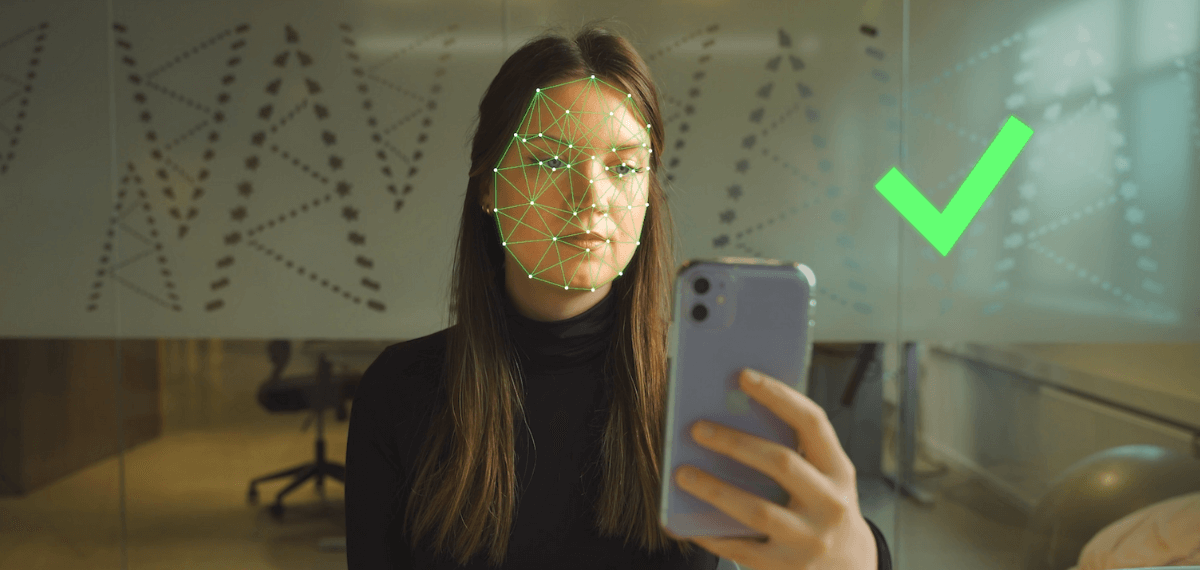

Facial recognition works by analyzing key features of your face, like the distance between your eyes, the shape of your nose, and the contours of your jaw. The system creates a unique template based on these features and uses it to identify or verify you.
Benefits: It’s quick, convenient, and non-intrusive. You don’t need to physically interact with the device, making it ideal for things like unlocking your phone or passing through security at airports.
Common challenges: It can struggle with changes in your appearance, like wearing glasses, hats, or a different hairstyle. Lighting and angles also play a huge role in accuracy, and it can be less reliable in low-light or poor-quality images.
2. Selfie Verification
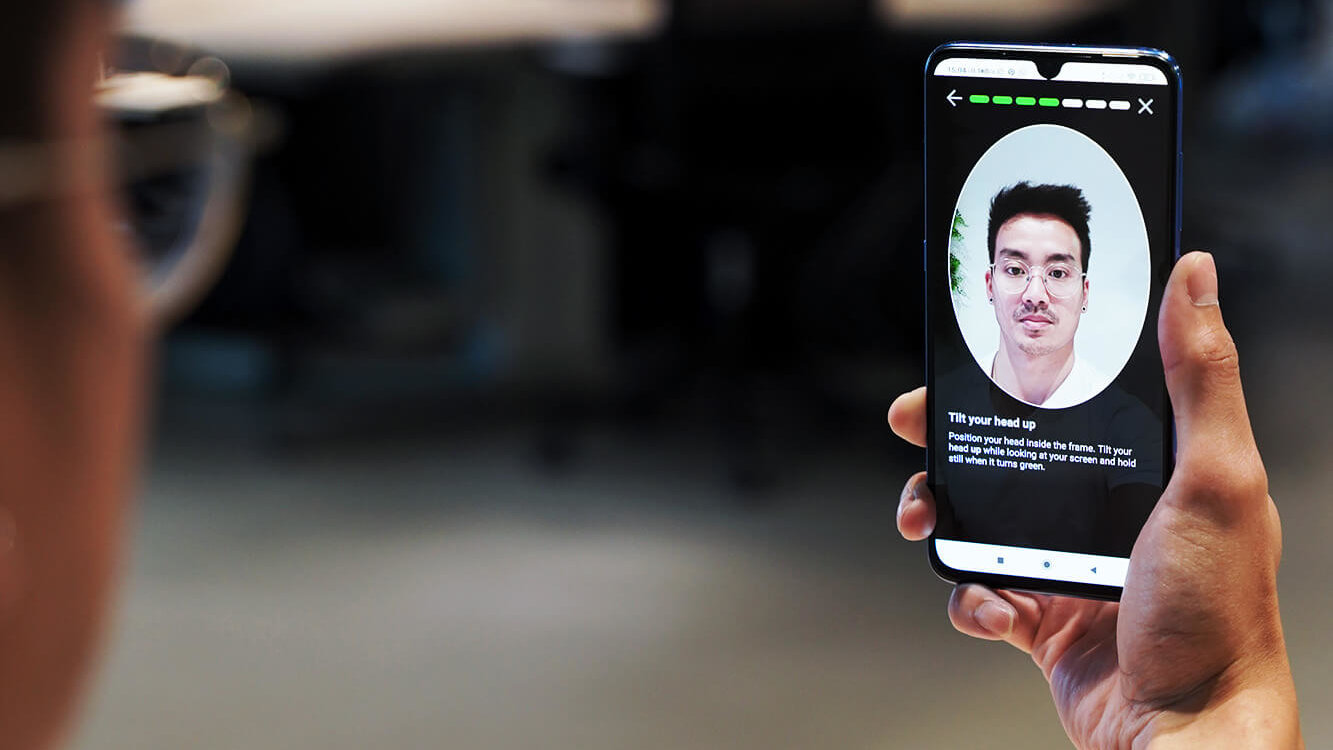


Selfie verification involves taking a photo of your face using a smartphone or camera and comparing it to an existing photo or a live image. It’s often used as part of a two-factor authentication process, where the system asks you to verify your identity by taking a quick selfie.
Benefits: Quick, easy, and widely used in mobile applications, especially for onboarding processes in banking or social media. It adds an extra layer of security while ensuring the user is present and actively participating in the authentication.
Common challenges: The quality of the selfie can be affected by lighting, angles, or device quality, making it prone to false rejections. It can also be vulnerable to spoofing techniques, like using photos or videos of a person to trick the system.
3. Fingerprint Scanning


Fingerprint scanning analyzes the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on your fingertip. The system stores this pattern as a template and matches it when you place your finger on a scanner.
Benefits: Fingerprint scanning is one of the most well-established and widely used biometric methods. It’s quick, and accurate, and is commonly found in devices like smartphones, ATMs, and security systems.
Common challenges: Dirty or damaged fingers can make it hard for the scanner to get a clear reading. Certain skin conditions or aging can also affect the quality of the print, and there’s always a risk of fingerprints being replicated with advanced technology.
4. Iris/Retina Recognition
Iris recognition looks at the unique patterns in the colored part of your eye, while retina recognition analyzes the blood vessels in the back of your eye. These patterns are incredibly unique and make this method highly secure.
Benefits: It’s extremely accurate, and because your iris and retina are unique, it’s almost impossible to replicate. Some systems can even capture your iris from a distance, offering a convenient and non-intrusive way to verify your identity.
Common challenges: This method requires you to position your face close to the scanner, which can feel a bit intrusive. It’s also sensitive to lighting and can be affected by things like wearing glasses or contacts, and some people find the process uncomfortable.
5. Voice Recognition
Voice recognition works by analyzing the unique qualities of your voice, such as pitch, tone, and the way you speak. The system creates a “voiceprint,” which it uses to verify your identity when you speak.
Benefits: It’s super convenient because it’s hands-free and can be used in phone-based applications or with virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa. Plus, it’s easy to integrate into customer service and banking systems.
Common challenges: Factors like illness, stress, or background noise can change the way you sound and potentially cause issues with recognition. Voice spoofing, where someone mimics your voice, is another security risk to consider.
6. Hand Geometry
Hand geometry measures the size and shape of your hand, including things like finger length and palm width. The system captures these features and uses them to create a unique template for identification.
Benefits: It’s non-intrusive and easy to use, making it a great option for physical access control, like in office buildings or secure areas. It’s also fast and doesn’t require specialized training to use.
Common challenges: While it’s good for basic identification, it’s not as accurate as other methods. It may not work as well for people with smaller or differently shaped hands, and because hand shapes are not as unique as fingerprints, there’s a greater chance of false matches.
Each of these methods offers different benefits depending on the application, but they all face certain challenges. The choice of which biometric to use often depends on factors like security needs, convenience, and the environment in which it’s used.
Biometric Authentication Use Cases
Biometric authentication has a variety of use cases across different industries. The main industries that already use biometric authentication are:
Financial Services
Biometric authentication can be used in financial services to prevent fraud, streamline transactions, and improve the customer experience. For example, banks can use fingerprint or iris recognition to authenticate customers at ATMs, to access the safe lockers behind the vault, or when making online transactions.
Retail
Biometric authentication can be used in retail to improve security, prevent identity theft, and provide a personalized shopping experience. For example, retailers can use facial recognition to identify known shoplifters.
Cryptocurrency
Biometric authentication can be used in the cryptocurrency industry. By using biometric authentication as part of the crypto KYC process, trading platforms can ensure that only verified users are able to access their platforms and conduct transactions, increasing the security of the exchange and reducing the risk of fraudulent activity.
Government
Biometric authentication can be used in the public sector for a variety of purposes, including identification, border control, and law enforcement. For example, law enforcement agencies can use facial recognition to quickly identify suspects and improve public safety. Another example is the use of fingerprint recognition in crime scene analysis.
Healthcare
Biometric authentication can be used in healthcare to verify patient identities, reduce medical fraud, and improve patient safety. For example, healthcare providers can use facial recognition technology to match patient photos with their medical records to ensure the right patient is receiving the correct treatment.
While these are the main use cases, biometric authentication offers numerous use cases across various industries. As the technology continues to improve and become more widely adopted, we can expect to see even more applications in the future.
Do you want to get started with biometric authentication? Have a look at Klippa’s solution and learn how we can help you with your biometric authentication processes.
Get Started With Biometric Authentication
Klippa’s automated identity verification solution is equipped with biometric authentication features and advanced technologies, including OCR, AI, machine learning, and computer vision. It can be used for digital customer onboarding and KYC checks.
You can integrate the software into your web or mobile applications with our Identity Verification SDK, enabling your customers to authenticate themselves using biometrics. This enables you to verify customer identities through biometric selfie scans, real-time liveness checks, and ID document verification using facial recognition.
Next to that, our software enables our clients to read RFID chips from identity documents using NFC ID verification technology. This technology uses encrypted data in the identity document’s chip to ensure 100% data accuracy and authenticity validation. Combining biometric authentication and NFC ID verification can help protect your organization from fraud attempts.
To help our clients stay GDPR-compliant, no data is stored on Klippa’s servers.
As the potential for cyber assaults grows, it is critical to deploy strong security measures to safeguard sensitive data. Klippa’s identity verification with biometric authentication offers an advanced method of verifying identities and authenticating users.
If you want to learn more about how biometric authentication can help you and your organization, our experts are always available to assist you in making the right decisions. Just schedule a demo below or contact us.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication offers a secure and convenient way to verify identity, with various methods available to suit different needs. Whether it’s through facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, or selfie verification, each method brings its own strengths and challenges.
As technology evolves, biometric systems will likely become even more integrated into our daily lives, providing enhanced security and user convenience. Choosing the right method depends on the specific use case, security requirements, and user preferences.