
Automation is on the rise as many companies are looking for better ways to process and store documents. Since traditional methods are not only time-consuming and error-prone but also fall short in meeting today’s data privacy and compliance standards, they don’t work anymore. So it’s only natural that more and more business documents decide to automate document processing and workflows.
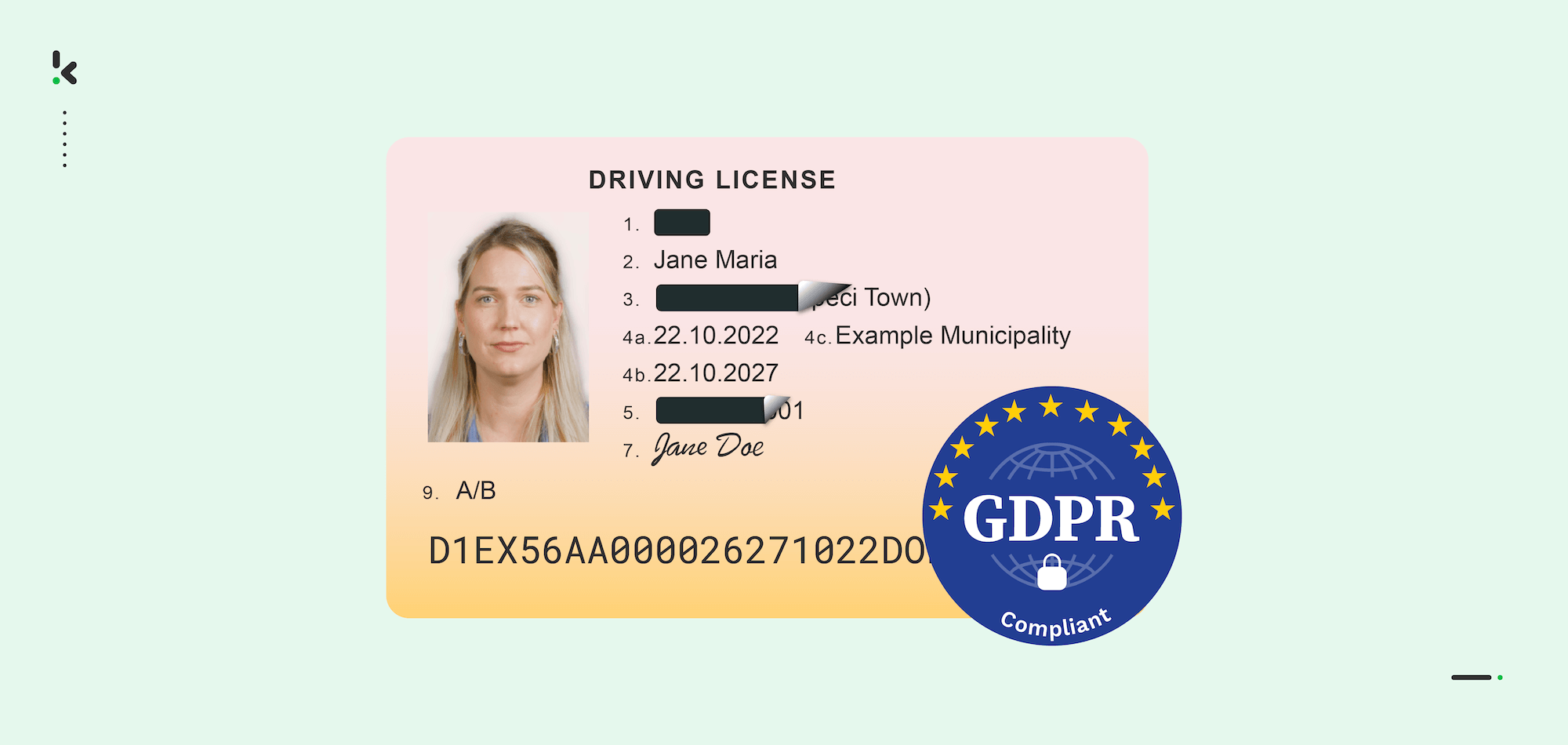
However, automation alone isn’t enough. One of the biggest challenges is compliance with the strict General Data Privacy Regulations (GDPR) imposed in May 2018. Although these regulations improve the protection of data and clarify the responsibilities of organizations, they don’t prevent data breaches altogether.
In fact, the costs resulting from data breaches increased from US$4.45 million in 2023 to US$4.88 million in 2024, which is a significant increase and the biggest jump recorded since the pandemic in 2020.
As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, companies must find solutions to protect the stored data better. An excellent solution to minimize data breach risks and ensure GDPR compliance is automated data masking.
This blog will cover what data masking is, how it works, and how Klippa can automate this process for you.
Key Takeaways
- Data masking is essential for securing Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), payment data, and other regulated information – whether in onboarding workflows, HR systems, or archives.
- Manual data masking is no longer sustainable. Automating it is a powerful solution that helps organizations protect sensitive data, comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Automation significantly improves speed, accuracy, scalability, and cost efficiency. In one example, automating the redaction of 100,000 identity documents reduced labor hours by over 1,100 and saved more than €20,000.
- Klippa’s DocHorizon platform offers full automation capabilities – including mobile SDKs, API integrations, and additional features like document watermarking – allowing companies to embed data masking into any workflow.
Want to skip straight to the steps? Click here to dive directly into the actionable steps to automate data masking!
What is Data Masking?
Data masking, also known as data anonymization, data redaction, or data obfuscation, is a security technique to mask sensitive data. It’s applied to avoid compromising the data and reduce security risks while complying with data privacy regulations.
For example, many organizations must perform Know Your Customer (KYC) checks within customer onboarding processes. To perform these checks to validate customers’ identities, entities must process identity documents.
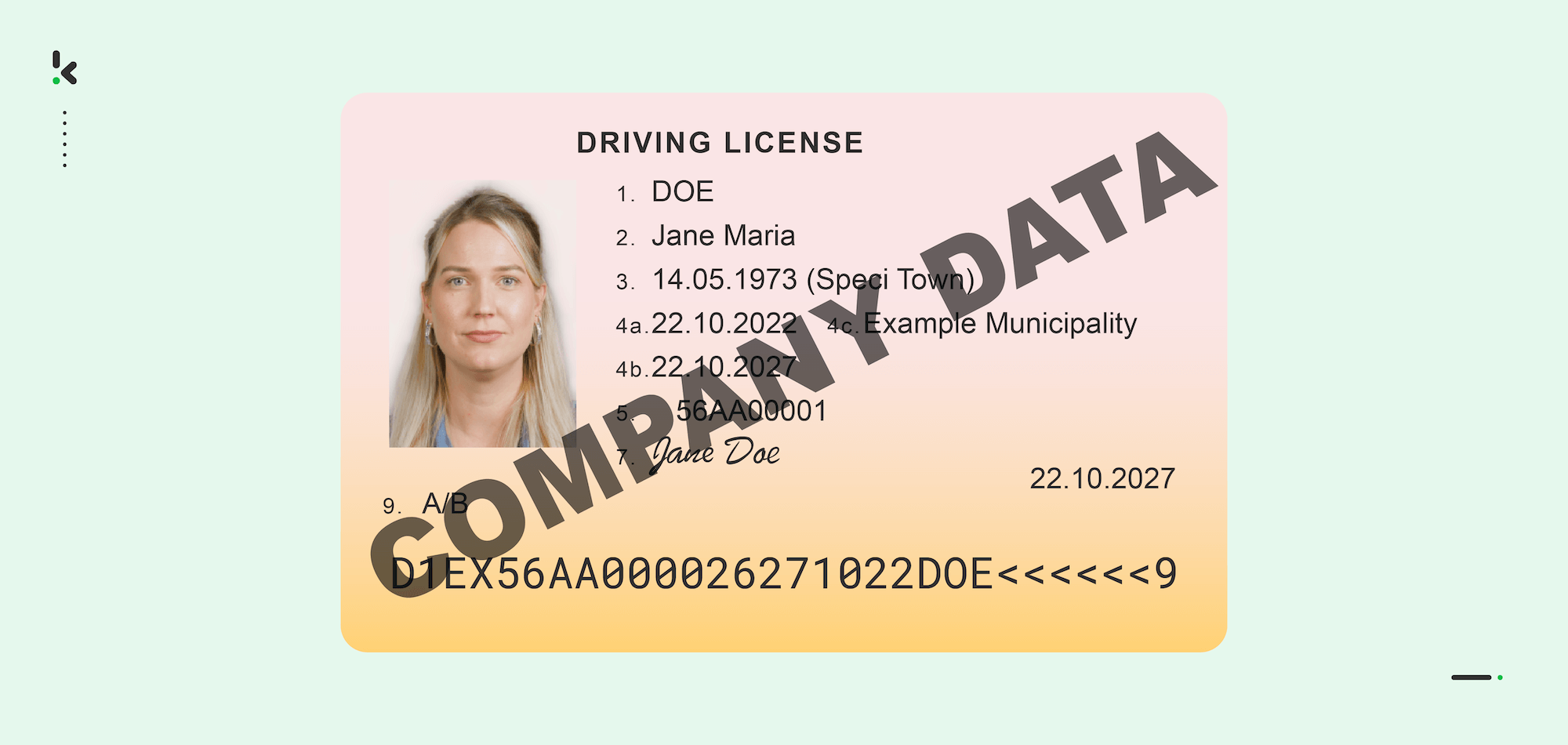
However, some information, such as social security numbers, cannot be stored under the GDPR. Although there are exceptions, most organizations need to anonymize or obfuscate the data to ensure compliance. Just like in the image below.

It’s interesting to note that, currently, data masking is gaining more traction, and the industry is estimated to grow from US$483.90 million in 2020 to US$1044.93 million by 2026.
From Manual to Automated: The Evolution of Data Masking
For as long as we can remember, manual document redaction has been used across various industries. It’s such a tedious task to perform, and it has so many underlying issues…
So, let’s face it. Manually redacting documents is not a scalable option (at least not if you want to be cost-efficient).
Luckily, it is possible to automate document redaction with today’s technology. There are two ways that organizations can capitalize on this:
- Fully automated data masking. No human intervention is needed. With technologies such as AI-powered Optical Character Recognition (OCR), it is possible to automatically recognize, locate, and redact the information field from documents.
- Human-assisted data masking. Human-in-the-loop (HITL) automation uses AI for automation and enables human personnel to do the final checks to verify data masking completion.
Choosing the appropriate solution is just one of the steps towards a successful data masking automation. In the next section, we’ll cover the necessary steps so you can feel prepared for such a big leap of faith.
How to Automate Data Masking?
Automating data masking doesn’t have to be complex or resource-consuming, especially with the new tools like intelligent OCR and powerful AI on the market. We present a step-by-step overview to guide you through the automation process, from initial planning to production-ready implementation.
Step 1: Identify Sensitive Data Fields
The first step is to map out which data fields must be masked by running a data audit across documents, databases, or incoming file flows. Sensitive data are typically personally identifiable information (PII) or regulated fields like social security numbers (SSNs), bank account or credit card numbers, dates of birth, or contact information (e.g., phone, email).
Step 2: Select the Right Automation Technology
Once you know what needs to be masked, choose the best tools for detecting and handling those fields. The technologies we recommend the most are Optical Character Recognition (for extracting text from images, scanned documents, and PDFs), AI-driven field detection (for identifying sensitive fields based on keywords, patterns, or context), and integration capabilities such as APIs or SDKs (for integration into your current systems).
Step 3: Choose the Appropriate Masking Method
Based on the use case and level of security required, select the masking techniques you want to apply. You can apply one or combine several techniques depending on your compliance needs and the types of documents being processed.
Options include techniques like redaction (blacklining or nulling out), substitution (pseudonymization), shuffling or scrambling, and data encryption (for high-security use cases). You can find out more about this in the next section.
Step 4: Configure Output Formats and Destinations
This is an important step as it ensures the chosen automation workflow gives you results that are compatible with your other systems. Decide what the output should look like and where it should go.
For example, you can ask yourself if the returned data should be returned in JSON or XML; if you need a copy of the masked document in PDF, JPG, or another visual format; or if the output will feed into your ERP, CRM, archive, or analytics platform.
Step 5: Test and Validate the Results
Before actually implementing automated data masking, run some tests to evaluate the accuracy of field detection and masking, the formatting and the structure of the output, and how special cases are handled. As an extra feature, you can also choose to implement a Human-In-The-Loop (HITL) step for manual review for documents with complex layouts or that are highly important, such as legal forms or health records.
We hope the steps above brought some clarity about how easy and simple it is to automate your data-masking processes. As promised, the next section will delve into how you can choose the masking technique(s) that are fit for you and your business.
Choosing the Right Masking Techniques
The right data masking approach primarily depends on the resources, use cases, and providers. Before diving into specific techniques, it’s important to understand the two main types of data masking:
- Static Data Masking (SDM) is used when data needs to be masked at rest. This means the sensitive fields are replaced with masked values, and the original data is altered and replaced permanently. This is ideal for testing, data migration, anonymized reporting environments, and protection against data breaches.
- Dynamic Data Masking (DDM) masks sensitive data in transit (i.e., actively used), leaving the original copy unaltered. With this approach, the unmasked data is visible in the actual database. DDM is often used when organizations send data to a third-party vendor or internal stakeholders who are not authorized to see sensitive data.
Now that the masking type is chosen, the next step is to apply the appropriate technique. Here are the most widely used data masking techniques.
Substitution
Substitution, or pseudonymization, is a technique to substitute the original data with random data from supplied or customized lookup files. It is useful when organizations need to preserve the authentic look of data while disguising sensitive data.
This technique can effectively protect data from breaches and help control internal access.

Shuffling
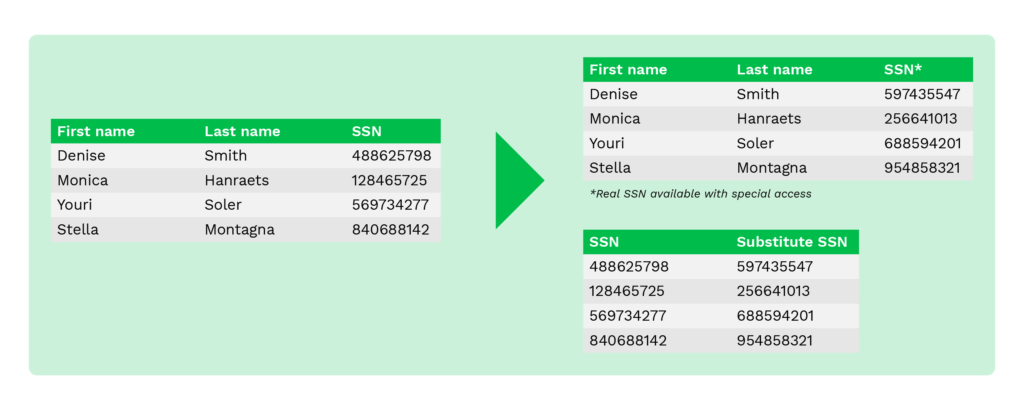
Shuffling is a technique similar to substitution. It is also used to substitute original data with other data that looks authentic. The difference is that the entities in the same column are randomly shuffled.
For instance, organizations can use this technique to shuffle employee name columns of multiple employee records randomly. Its disadvantage is that it can be prone to reverse engineering if anyone gets their hands on the shuffling algorithm.

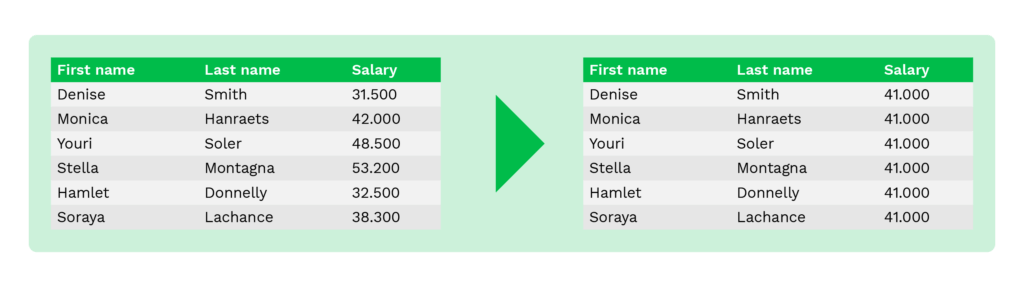
Averaging
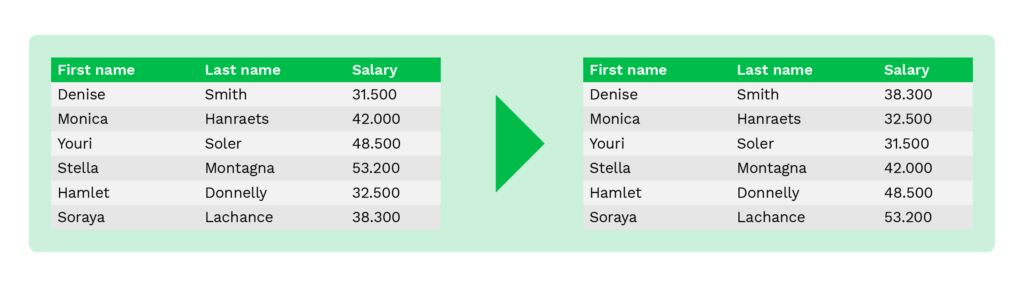
Averaging is a method to replace original values with an average value of the table columns. For instance, instead of showing salaries or account balances of individuals, the initiator shows only the average value of wages or account balances.
This method helps maintain the aggregate value and is commonly used for statistical analysis or data collection purposes of financial institutions.

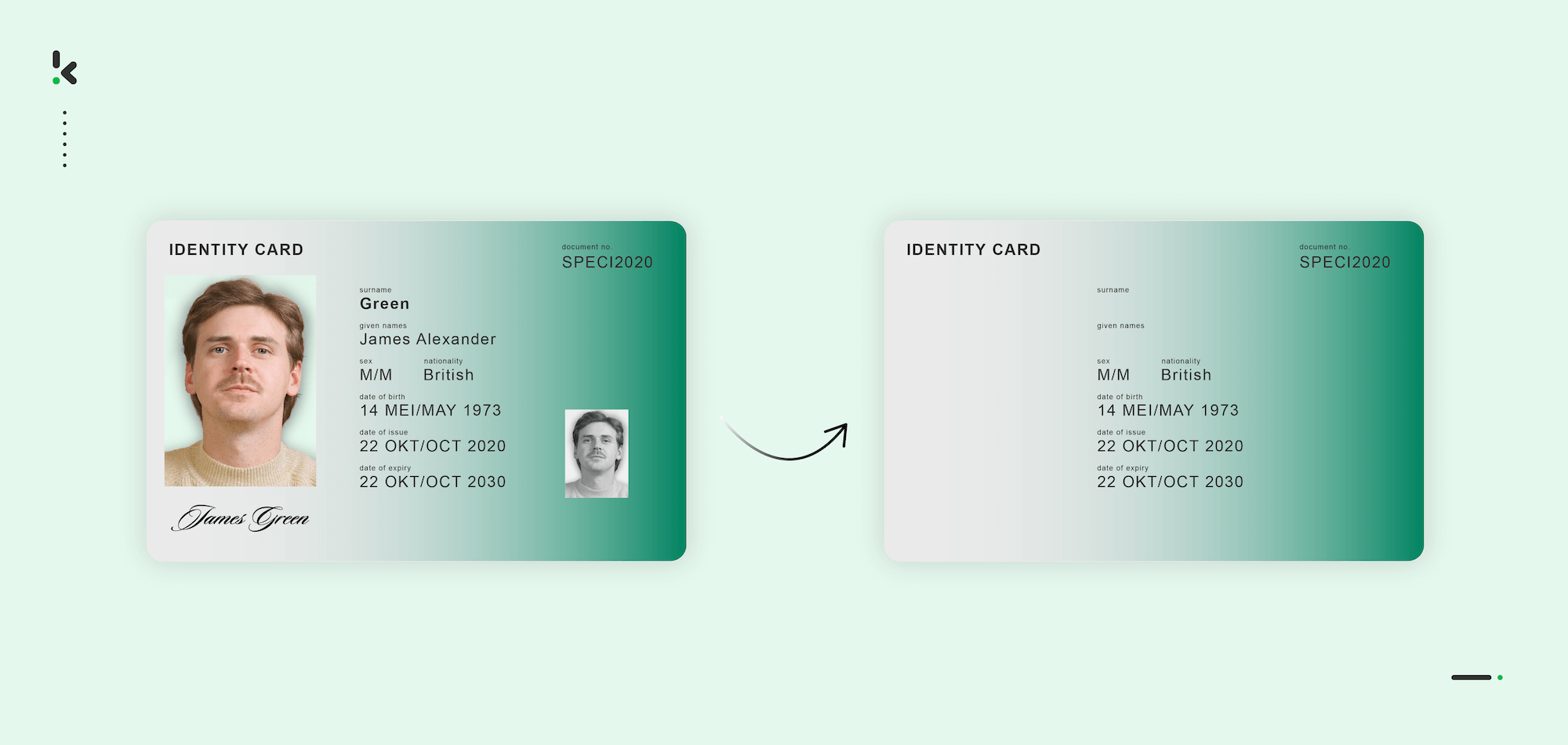
Nulling out (Deletion)
Nulling out is a technique to replace sensitive data with a null value to prevent unauthorized users from seeing the original data. It simply means removing the information or replacing it with an empty value on documents.
In some use cases, information on certain documents is left out entirely, such as the date of birth on resumes. Often, this is done to eliminate the risks of unethical hiring practices.

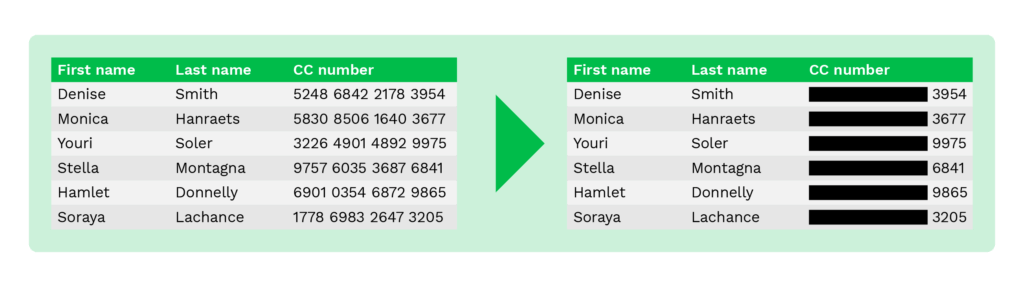
Data Redaction (blacklining)
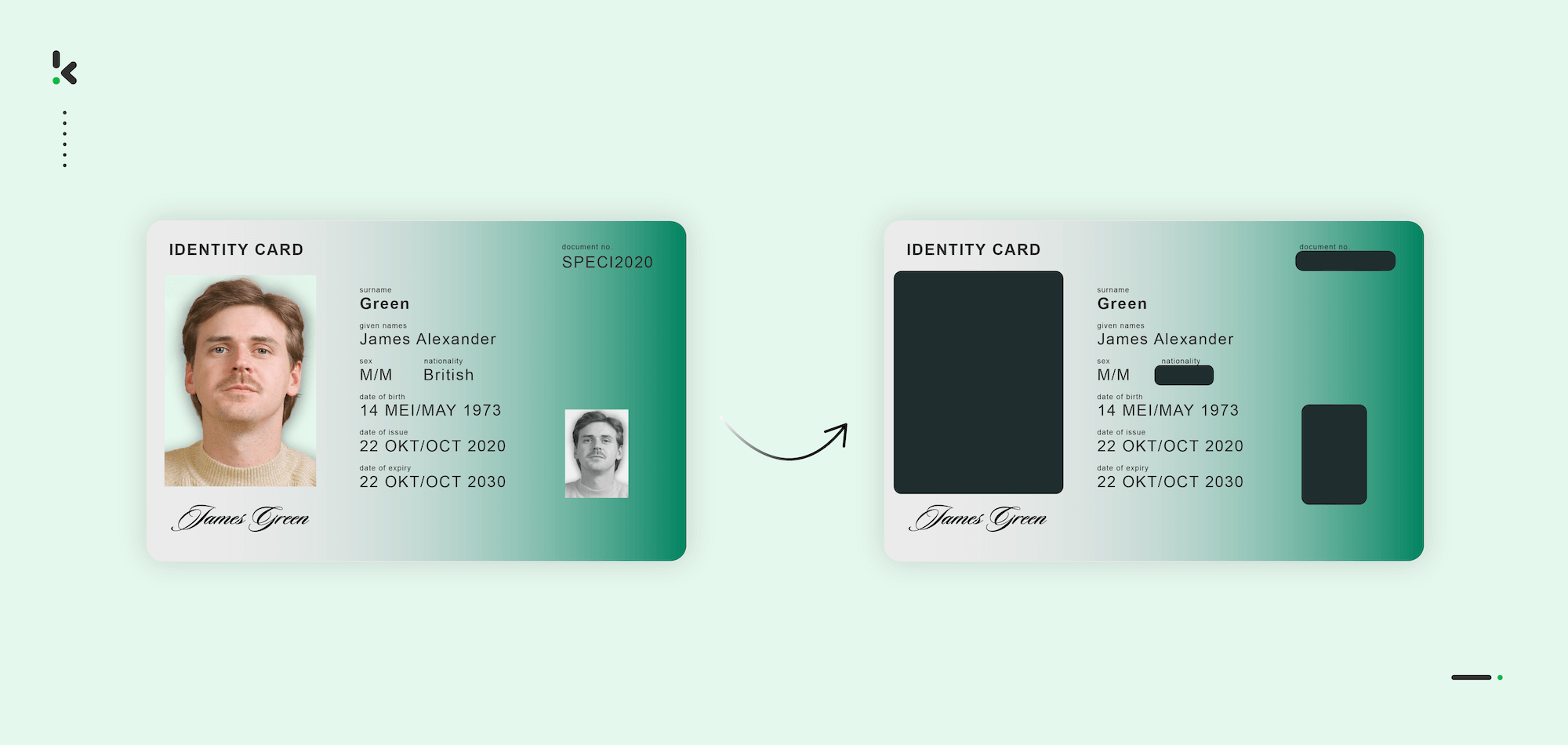
Data redaction, also known as blacklining, is a method similar to nulling out, as only some part of the original data is masked. For example, to prevent fraud, only the last four digits of the payment card number are shown to customers while online shopping.
The same method can be applied to any document containing privacy-sensitive information. Below, you can see an example where several fields are redacted.

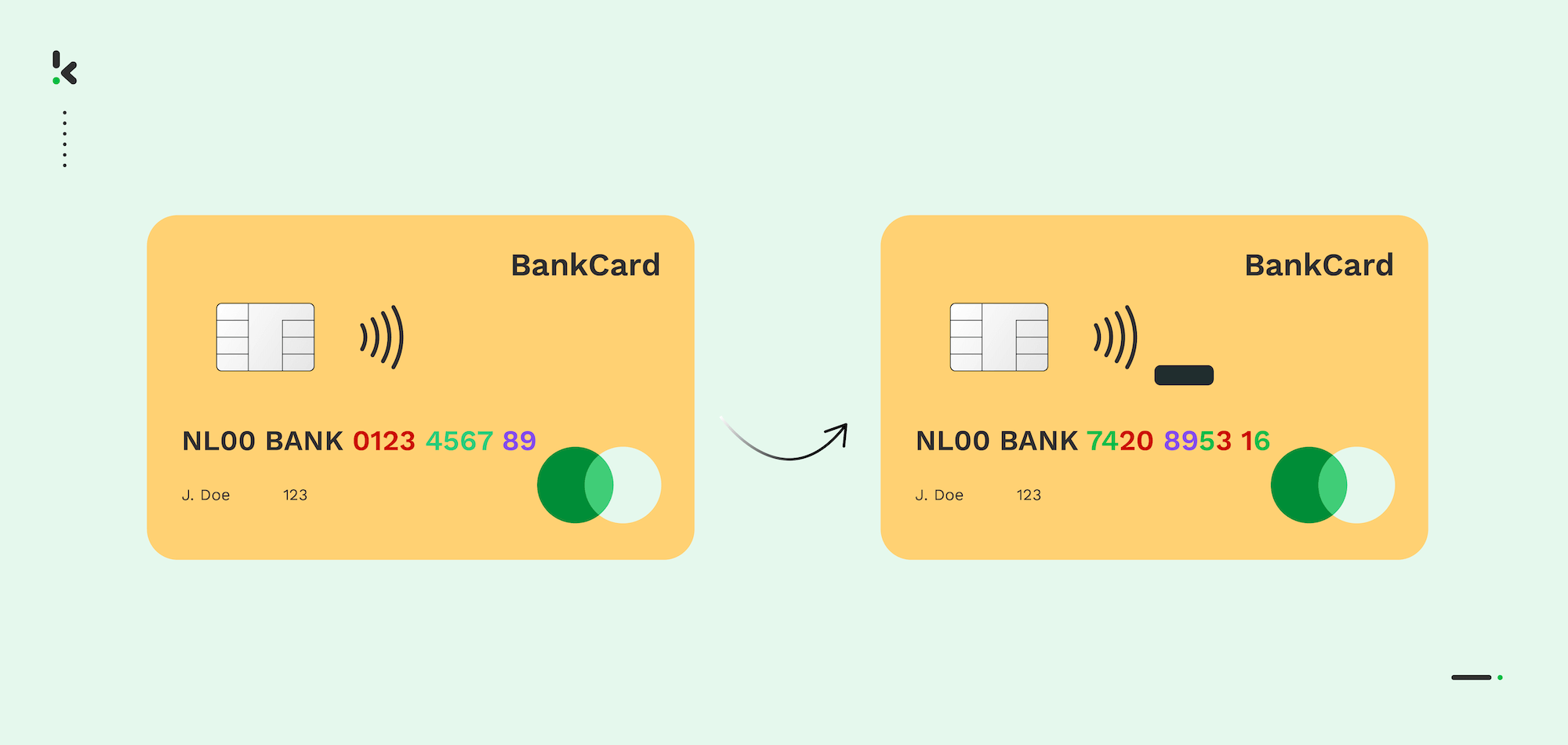
Data Scrambling
The data scrambling technique alters data by randomly rearranging the order of characters or numbers with a specific algorithm. The original data can no longer be obtained after completing the process, as the data is scrambled.

Data Encryption
Data encryption is a technique that allows access to data only with the decryption key. It is the most complex data masking algorithm and the most secure one. In addition to the complexity, proper encryption key management is required to ensure security.

So why should your organization automate data masking? Let’s dive into the benefits that come with it.
Benefits of Automated Data Masking
While organizations can safeguard data from leaks and ensure GDPR compliance with data masking, automating it adds many more benefits. These benefits include:
- Faster turnaround times – Automating document or data redaction enables your workforce to focus on more important tasks and complete more tasks in the same amount of time. Also, fewer people would be needed to complete these tedious tasks.
- Accuracy – With an automated data-masking solution that uses AI, businesses can achieve higher accuracy simply because machines and computers don’t get tired.
- Speed – With an automated solution, the data redaction process can go up to 90 times faster. You can see a simplified calculation in the following section.
- Cost savings – With higher efficiency and accuracy achieved with AI, organizations can significantly save money (labor hours, reduced mistakes, etc.).
- Scalability – There is a limit to how many documents an average employee can redact. Data masking automation offers businesses a way to redact documents at scale without increasing operational costs.
It seems like there are many benefits that organizations can enjoy from an automated data masking solution. But what does it mean to you in terms of business?
Overall, data masking provides impressive benefits, which can help businesses gain a competitive advantage. But what are the common use cases? Let’s have a look at some of them.
Use Cases of Data Masking
There are many use cases for data masking, including the following ones.
Blacklining Payment Card Numbers
Under some circumstances, a member of your organization might need access to credit card or payment card information. Therefore, using data masking to blackline the last four digits of the card number can prevent exposure to sensitive components such as payment card numbers.
It is a widespread method for banks and other financial institutions to handle their customers’ payment information. By blacklining the payment card number, organizations can ensure compliance with the PCI-DSS.

Anonymizing Social Security Numbers
Information such as the SSN on identity documents such as passports and ID cards is highly sensitive. Often, organizations outside governmental institutions are not allowed to store the SSN in their database.
In the Netherlands, the burgerservicenummer (BSN) is equivalent to the SSN. The BSN is a unique personal citizen service number used to identify each registered citizen. For instance, the BSN is used by government institutions to find data from each citizen, often for tax purposes.
SSNs and BSNs are strictly prohibited under the GDPR as they belong to “special categories of personal data.” Of course, there are cases where storing such data is allowed. But only with a special legal exception or consent from the person.
Therefore, it is common to anonymize SSN or BSN numbers using various data-masking techniques.
Resume Redaction
Despite all the training to reduce bias in the hiring process, a high number of recruiters are guilty of basing their decisions on different biases. Unfortunately, it is still common that if two candidates have similar skill sets and experience, the more attractive one will be hired.
To combat this, organizations have started to automatically redact resumes to eliminate biases and discrimination in the early stage of the recruitment process. The most common fields that are redacted from resumes include home address, name, and picture.
With data masking, recruiters are better supported in evaluating candidates solely based on their skills and experience. It is important to note that recruiters are only human, after all.
Masking Data for Digital Archiving
Storing paper-based data is no longer an option for many organizations. The reasons for organizations to move towards digitization with the advancement of technology include:
- An enormous backlog of unorganized data
- Internal access control
- Time and cost savings
- Environmental friendliness
- GDPR compliance
- Easy data accessibility
While data archiving can be highly beneficial, its challenge is to meet legal obligations concerning data privacy laws. In this respect, data masking is a secure and solid solution to ensure GDPR compliance.
Before archiving, companies can simply use data masking to redact all sensitive parts such as names, patient numbers, and social security numbers from documents or substitute them with structurally identical data (same amount of numbers or characters).
Organizations have adopted this method in industries such as legal and healthcare, to name a few.
Now that we have covered a few of the use cases, let’s take a look at how Klippa and its features can help you achieve seamless automated data masking.
Automate Data Masking with Klippa

Our Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solution, Klippa DocHorizon, is designed to help organizations digitize, extract, classify, verify, and anonymize data from various documents.
With Klippa DocHorizon, your organization can reduce turnaround times, costs, and human error while safeguarding sensitive data.
While our AI-based OCR software includes data masking capabilities, we have developed several features to enable integrations with our clients’ existing document management systems and to enable them to leverage our technology within their systems, such as:
- Data Masking API: We have developed a data-masking OCR API to enable our clients to blackline certain fields and pictures from documents. Currently, our data-masking OCR API is made available through a RESTful API, enabling our clients to integrate it into web-based applications. To help our clients, we provide clear documentation.
- Data Masking on Mobile: We also offer a mobile scanner SDK with data-masking functionalities to mask certain information documents. Currently, our scanner SDK is available for both Android and IOS. Wrappers for cross-platform languages like ReactNative, Flutter, Cordova, and Nativescript are also available.
- Watermarking Documents: If data-masking is not possible, Klippa also offers digital document watermarking as an alternative. This way, you can protect the copyright of your documents, enable your clients to share data more securely, and reduce security risks while storing sensitive data.
Whether you are looking for an end-to-end solution or an API / SDK integration to automate your document processing, Klippa is here to help. Fill in the form below for a free demo, or contact our experts to see how Klippa can support you.
FAQ
Encryption transforms data into unreadable code that requires a decryption key. Masking, on the other hand, permanently alters data into a fake but usable form and is typically irreversible. Encryption is ideal for security; masking is best for privacy in non-production use.
Absolutely. Data masking is one of the most effective tools for complying with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS by anonymizing or pseudonymizing personal and regulated data.
Klippa offers AI-powered document processing with built-in data masking. Our solutions can redact, anonymize, or pseudonymize sensitive data in real time using OCR, rule-based logic, and integration-ready APIs.
Yes, Klippa can easily handle bulk document anonymization. It can process and anonymize thousands of documents per hour, making it ideal for enterprises needing batch document redaction or high-volume compliance workflows.