

Companies today rely heavily on documents like PDFs, scanned images, and photos exchanged through emails or platforms.
But how often do you question the authenticity of these files? A simple photo of a damaged product or a screenshot of a bank transfer could be digitally altered in ways that are hard to spot. With tools like Photoshop and AI-generated edits becoming more accessible, the risk of image tampering is growing.
If you’re concerned about verifying the legitimacy of the documents you receive, you’re not alone. Fortunately, automated image tampering detection software can help.
In this blog, we’ll explore different types of image tampering, how to spot them, and solutions that can help safeguard your processes.
Key Takeaways
- Image tampering such as copy-move or splicing attacks, can be carried out in ways that are challenging to detect with the naked eye.
- Advanced technologies, like noise inspection, copy/move detection, and splicing detection, offer efficient ways to identify image tampering.
- Free online tools like Fake Image Detector are suitable for analyzing small amounts of documents or for occasional use.
- Premium tools such as Klippa provide advanced capabilities, enabling automatic detection of image tampering within seconds.
What is image tampering?
Image tampering, also known as image forgery, refers to the manipulation or alteration of images with the intent to deceive, mislead, or misrepresent information contained within the image.
Techniques such as copy move, splicing, inpainting, or deepfakes, can add, remove, or modify elements, creating misleading visuals.
Types of image tampering
Image tampering, can be performed in various ways. Let’s explore the different types of manipulations that fraudsters might use.
Copy move or photomontage
Copy move or photomontage is a type of image manipulation in which a region from one part of an image is copied and pasted onto another part of the same image to hide information or create a false appearance. It involves duplicating and placing an object in a different location to conceal or add elements to an image.
Attack example:
For instance, a sales representative returns from a business trip and wants to claim his expenses. He or she could copy a “1” from the receipt and paste it in front of the total amount “10”, making it suddenly an expense of €110, making it appear that the expenses are much higher than they are.
Splicing
Splicing is a technique where different parts of multiple images are combined to form a single, deceptive image. This type of tampering often involves merging multiple photographs or altering the content of individual photographs to create a misleading representation of an event or object.
Attack example:
Imagine someone who wants to trick an insurance company by submitting a fraudulent claim. They could merge different images to create a composite picture, combining various damaged properties or accidents to back up their claim and potentially receive a larger insurance payout.
Inpainted
Inpainted images involve the removal or alteration of objects or areas within an image by filling in the gaps with newly created, artificial content. The goal of this technique is to ensure that the inpainted sections blend seamlessly with the rest of the image, making it challenging to detect any modifications.
Attack example:
For instance, let’s consider property fraud. A person might try to manipulate real estate photos to mislead potential buyers or tenants. They could remove or alter undesirable features in the images, such as structural damage or unattractive surroundings, to make the property seem more appealing than it is.
Deepfakes
Deepfakes refer to manipulated images or videos in which the face or appearance of a person is replaced with someone else’s using deep learning techniques. These sophisticated forgeries can make it appear that someone said or did something they didn’t. Deepfakes have raised concerns about the potential for misinformation and fake content.
Attack example:
What if someone’s trying to open a bank account in another person’s name? They could use deepfakes to create counterfeit identification documents during the onboarding process. By generating a manipulated photo of themselves on a fake driver’s license, they can replace the original photo with theirs, allowing them to pass as someone else. This deception could easily enable them to open a bank account without raising suspicion from bank employees.
There are many ways to tamper with images, and it can be frightening. However, some technologies have been developed to detect these alterations easily. Let’s explore what they are.
How to Detect Image Forgery
With advancements in technology, detecting image forgery has become better. Various techniques are now available to identify and analyze manipulated images, ensuring authenticity and accuracy. Below are some effective methods software can utilize:
Noise inspection
In digital images, noise refers to random variations in color and brightness that are introduced during the image capture process. It can appear as specks, graininess, or distortions in the image. Think of it as the “grain” you sometimes see in photographs taken in low-light conditions.
How it works:
Noise inspection looks for inconsistencies in the patterns of noise across an image. Normally, noise should be consistent throughout an image. However, when tampering occurs, the noise patterns might not match or be consistent within certain parts of the image. By analyzing these inconsistencies, algorithms can detect areas that have potentially been tampered with.


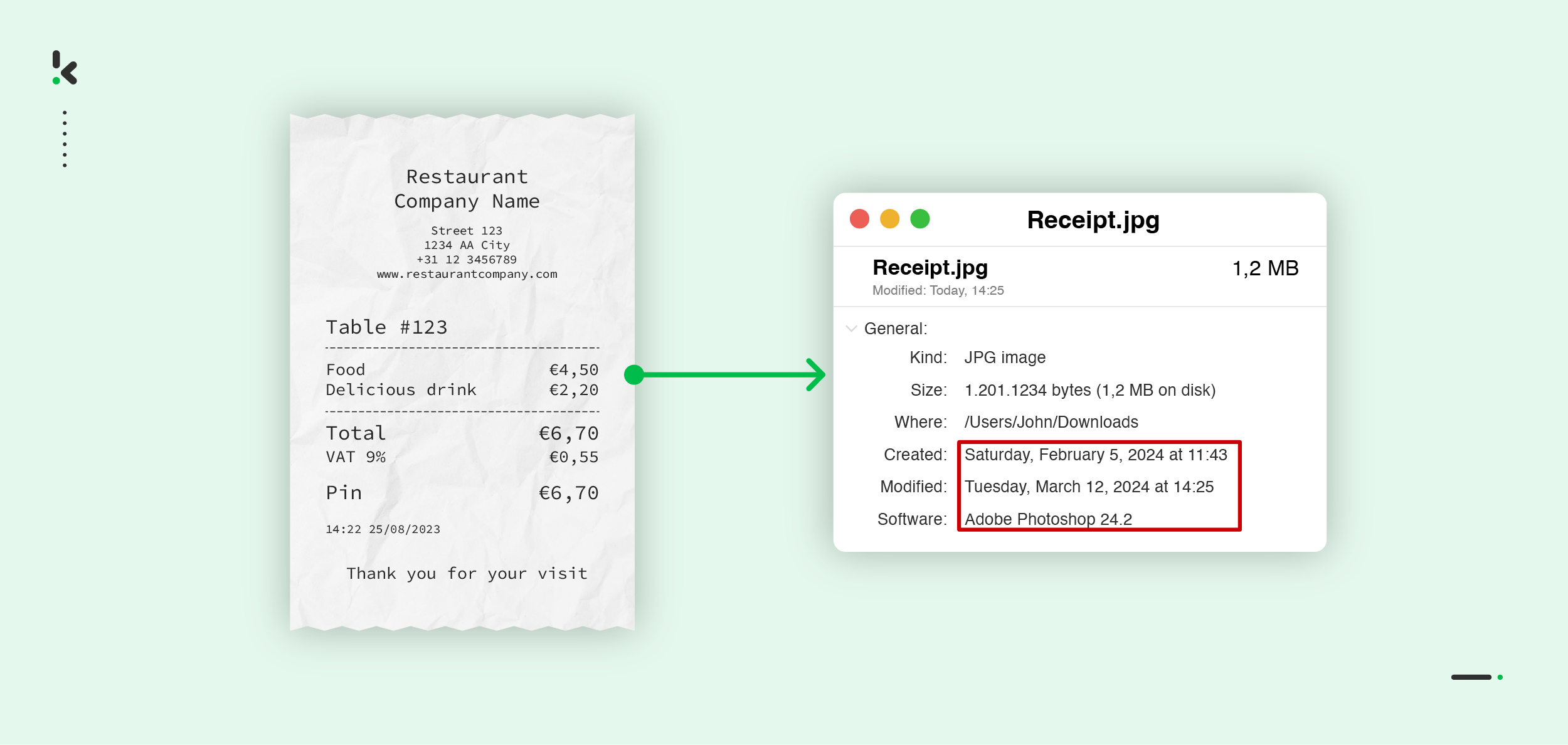
EXIF analysis
EXIF data is metadata embedded within digital images that contain information about the camera settings, date, and other details related to the image capture. It’s like a set of details about the image.
How it works:
EXIF analysis examines this metadata to identify any discrepancies that could indicate tampering. For example, if someone alters the date on a receipt to a future date, the EXIF data might show that the image was taken before the purchase even occurred. Similarly, missing or altered metadata could also raise suspicion of tampering.

Copy move detection
Copy-move detection techniques aim to identify duplicated or moved objects within an image.
How it works:
Copy/move detection algorithms analyze the patterns, textures, or visual features of different regions to identify if any objects have been copied, pasted, or moved around. By comparing these characteristics, inconsistencies or repeated patterns can be detected, suggesting tampering.
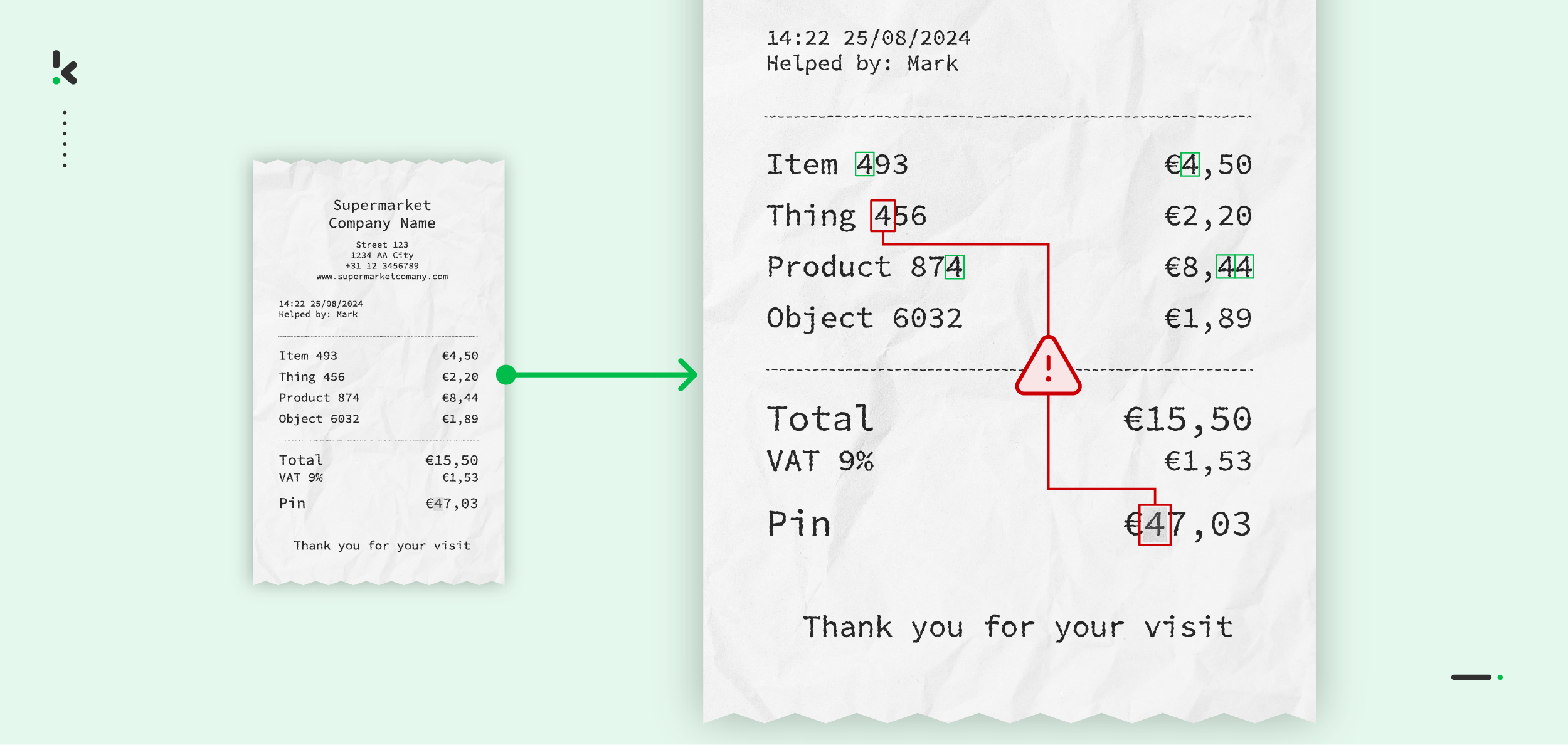

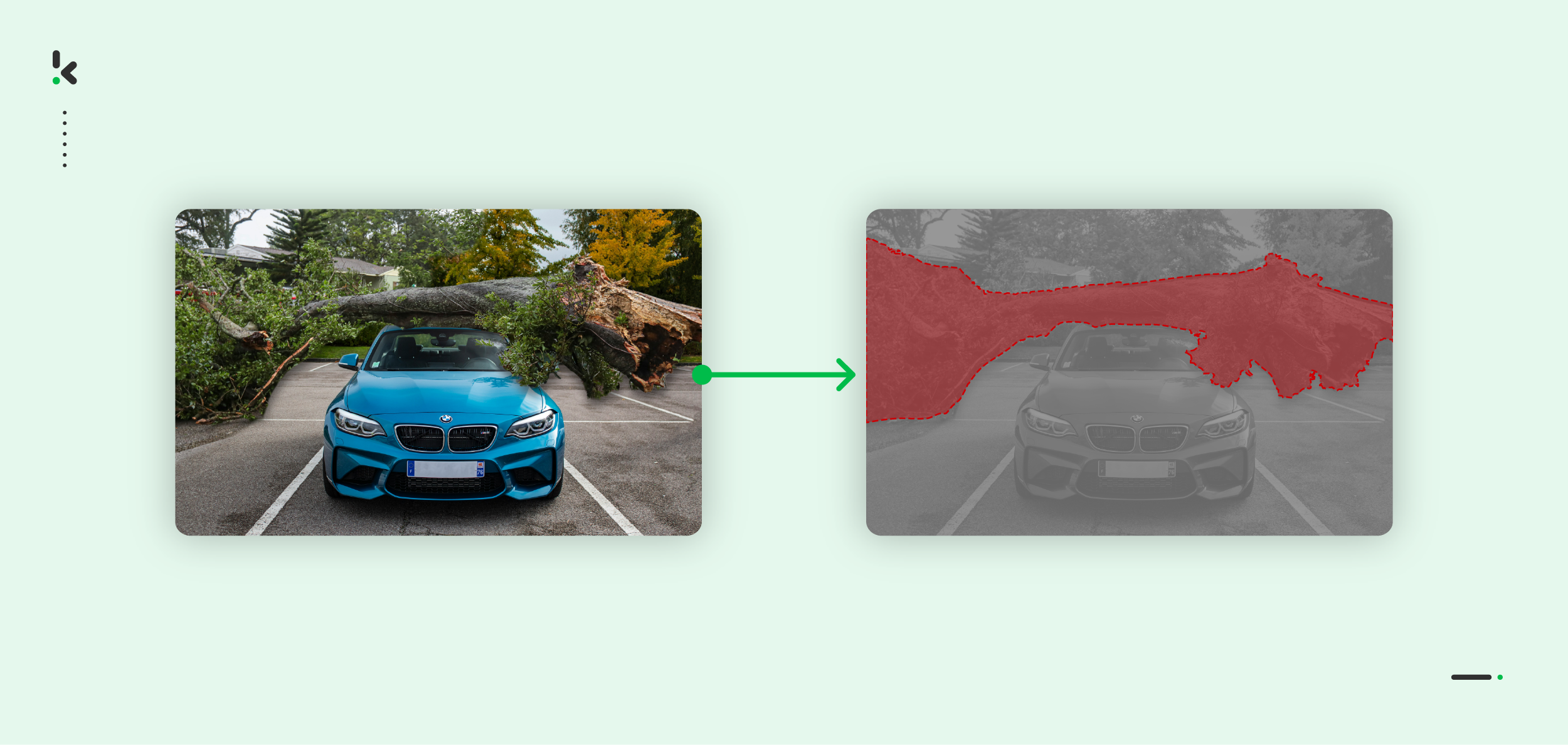
Splicing detection
Splicing detection methods aim to identify areas within an image where different parts from separate images have been merged.
How it works:
Splicing detection algorithms analyze the visual characteristics, such as lighting, shadows, textures, or other cues, to identify regions with abrupt transitions or inconsistencies. These irregularities suggest that the image might have been tampered with by combining different parts.


These techniques are commonly used in image tampering detection software to protect companies from fraudsters. Several free online tools are available if you need to verify a few documents or images.
Free tools to detect image forgery
Free online tools to detect image manipulation can be a good option for a low amount of documents. You could consider the tools below:
For occasional use, free tools can be practical; however, they come with limitations. These include a lack of bulk upload options and the need for manual inputting. Additionally, privacy concerns can pose risks for businesses, especially given the strict regulations like GDPR.
For organizations with more advanced requirements, premium solutions such as Klippa DocHorizon are available. These premium tools offer higher accuracy, increased scalability, and enhanced security, making them ideal for businesses that need improved performance in tasks like image tampering detection.
Detect Image Tampering Automatically with Klippa
Klippa DocHorizon is a premium solution designed for automatic detection of image tampering. It employs three methods to identify fraud related to image forgery, protecting you from fraudsters: copy-move analysis, metadata analysis, and splicing detection. At Klippa, we ensure that any documents you handle are legitimate, providing you with protection against fraudulent activities.
In addition to automated image tampering detection, Klippa offers numerous benefits for your company:
- Bulk document upload: Verify the authenticity of multiple documents simultaneously on a large scale.
- Custom Workflows: Set up your document workflows according to your needs by simply connecting any relevant DocHorizon modules: data extraction, capture, classification, conversion, anonymization, verification, and more.
- No manual intervention needed: Our platform can automatically retrieve documents from emails or any tools you use, process them, confirm their authenticity, and organize them as you prefer.
- GDPR and ISO certification: Enhance security for your company and your partners.
- High accuracy across various document types: Our solution delivers high accuracy for a wide range of document types, including financial documents and IDs.
So are you ready to go forward with fraud detection automation? Contact our experts today and let Klippa walk you through the process.
FAQ
Yes, Klippa uses AI technologies such as computer vision, machine learning, and deep learning to detect document fraud. These technologies work alongside OCR to automate document processing and enhance fraud detection.
Yes. Klippa offers a free trial with €25 in credits, allowing you to explore the platform’s features and capabilities before deciding.
Absolutely. Klippa complies with global data privacy standards, including GDPR. Your data is encrypted, securely processed, and never shared with third parties without your consent.