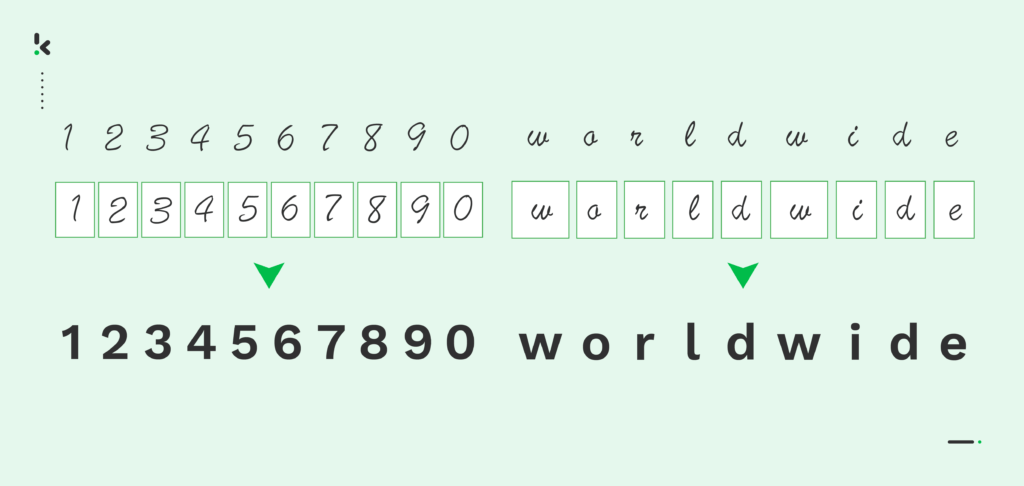

Doing more with less is an often-heard goal in management teams and company boards. Whether they are automating workflows or simplifying processes, organizations are always looking to gain efficiency and drive savings.
An Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solution accomplishes these goals by helping employees to work smarter, execute faster and increase their productivity.
The importance of these technologies cannot be underestimated. A 2018 Goldman Sachs report, for example, revealed that businesses spend $2.7 trillion on manual, paper-based payment processing, which is a big burden in terms of time and money.
This is a big problem for companies dealing with large amounts of paper documents. As the number of documents that need to be processed increases every year, companies cannot simply keep hiring more people to process if they want to keep a healthy bottom line. This leads to scalability issues.
Luckily there are technologies that can help companies deal with these issues such as Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR). ICR is used to extract text from images or scanned documents, such as receipts and invoices, and works similarly to Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
But how can this technology benefit your organization? And what are the differences between traditional OCR and ICR?
In this blog, you’ll find the definition of ICR, learn about the differences between OCR and ICR, find out how ICR works, and how it can be used. Curious? Let’s start!
What is ICR?
To put it simply, Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) is a technology used for extracting handwritten text from image files or documents and converting it into a machine-readable format.
ICR is technically a variant of Optical Character Recognition. That’s why it can sometimes be referred to as OCR.
However, in contrast to OCR technology which focuses on printed or computerized characters, ICR uses Machine Learning and AI to recognize various handwritten styles and fonts. For that reason, it can be seen as an advanced version of OCR.
ICR technology upgrades its learning capabilities every time new handwritten patterns are used. This way, data accuracy can be enhanced over time.
As mentioned above, ICR can often be confused with OCR and vice versa. The next section is dedicated to helping you understand the differences between the two.
Differences between ICR and traditional OCR
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) share many similarities, which is understandable given that ICR is a subset of OCR.
However, comparing ICR with traditional, template-based OCR like Zonal OCR is a different story. These two technologies significantly differ from each other, as illustrated below.
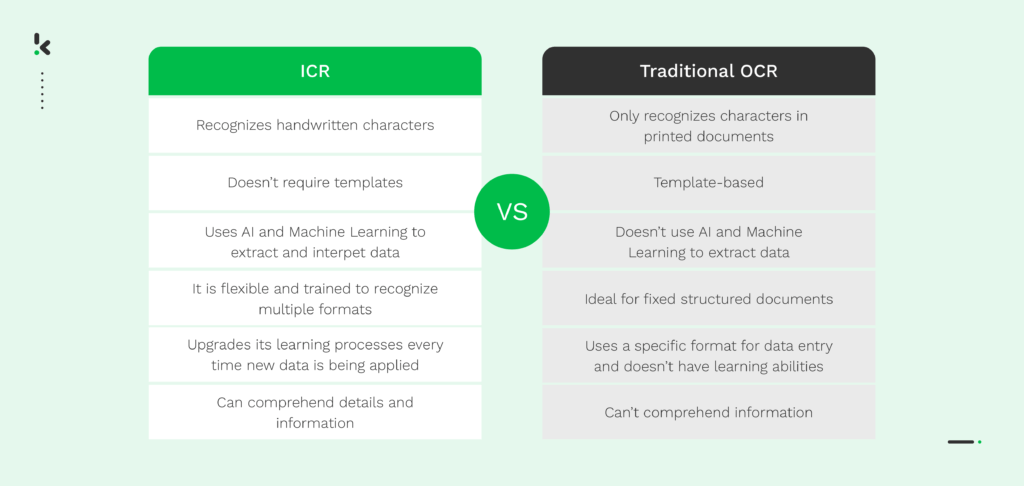

In a nutshell, Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) makes it possible to convert handwritten text into data that is simple to understand by a machine, search for, and change. Unlike traditional OCR, ICR uses AI and Machine Learning to understand details and extract information within the documents, thus making it easy to integrate into various business workflows.
ICR is an excellent addition to your data-capturing process if you deal with a lot of handwritten documents that contain both structured and unstructured information.
But how does it function? Learn more about it in the next section.
How does ICR work?
Intelligent Character Recognition software works similarly to OCR in recognizing characters. The only difference is that ICR can recognize handwritten characters, which traditional OCR cannot.
To better understand how ICR tackles those problems, let’s examine the following ICR process steps in more detail:
- Step 1: Image pre-processing
- Step 2: Segmentation
- Step 3: Recognition
- Step 4: Post-processing of the output
Step 1: Image pre-processing
Typically, raw data cannot be processed directly. In order to accurately extract data from documents, images must first be pre-processed. This means that the quality of the image has to be improved to achieve an acceptable form for recognition.
Many techniques are used during the pre-processing stage to provide a clearer and better image. These techniques may include:
- De-skewing – The process of straightening and adjusting an image’s angle after it has been scanned.


- Noise removal – This strategy includes the removal of background textures, interfering strokes, and other similar elements, as well as changing the intensity range of individual pixels to match the average values of the pixels around them.


- Binarization – Often referred to as image thresholding, binarization is the process of turning a grayscale image into a black-and-white one. This technique makes it possible to more precisely separate text from the background.


- Normalization – This process aims to eliminate slant and slope occurrences. These terms refer to the inclination at a character level (slant) or at a word level (slope), as you can see in the following image.


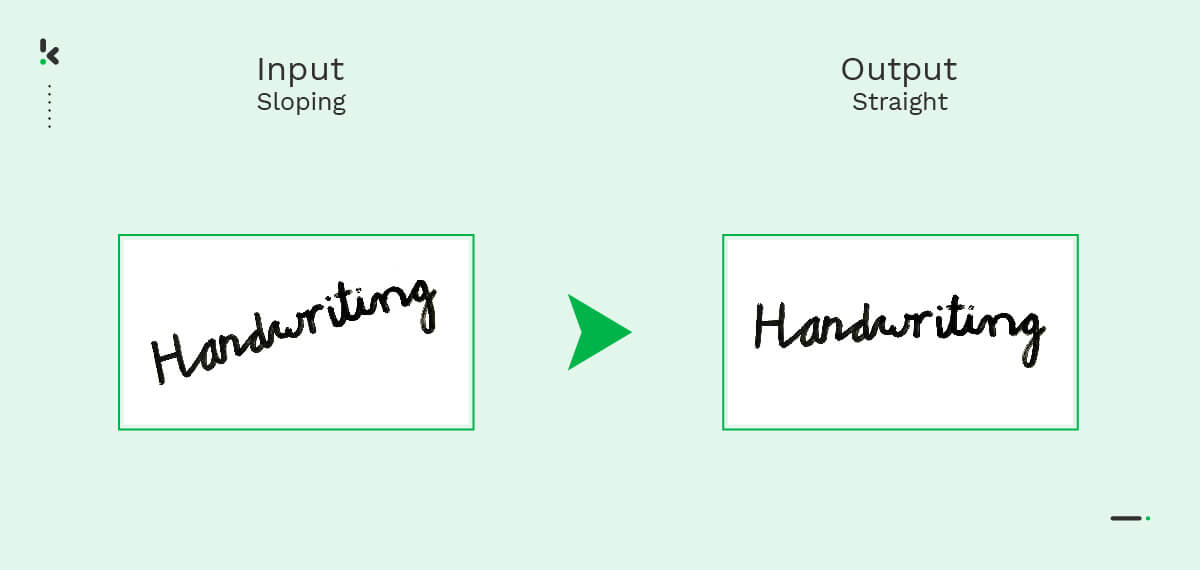

The end result of the pre-processing stage must be a clear image with easily identifiable characters and no distracting elements.
Step 2: Segmentation
Segmentation is the process of separating information within the text to make further data analysis easier. These categories are involved in this technique:
- Line segmentation – The isolation of the text lines in the image.


- Word segmentation – The isolation of the words in the text lines.


- Character segmentation – The isolation of characters in the words.


Step 3: Recognition
After segmentation, the isolated word fragments are recognized. This process is done through pre-trained models, which means that the characters are recognized by using a pre-existing database as a point of reference.
This works by giving a score for each character. Typically, the recognized character is the one with the highest score, when compared to the ones within the predetermined database.
As previously mentioned, ICR has learning abilities, meaning that it enhances its accuracy every time new handwritten styles and fonts are uploaded to the system.


Step 4: Post-processing of the output
This step is crucial to enhance the accuracy of data extraction since it focuses entirely on the methods and algorithms that produce the best results.
After proofreading and checking for spelling mistakes, ICR indicates anomalies (if detected) for the user to fix.
Once the data has been corrected and accurately labeled, it can be stored in a database of choice.
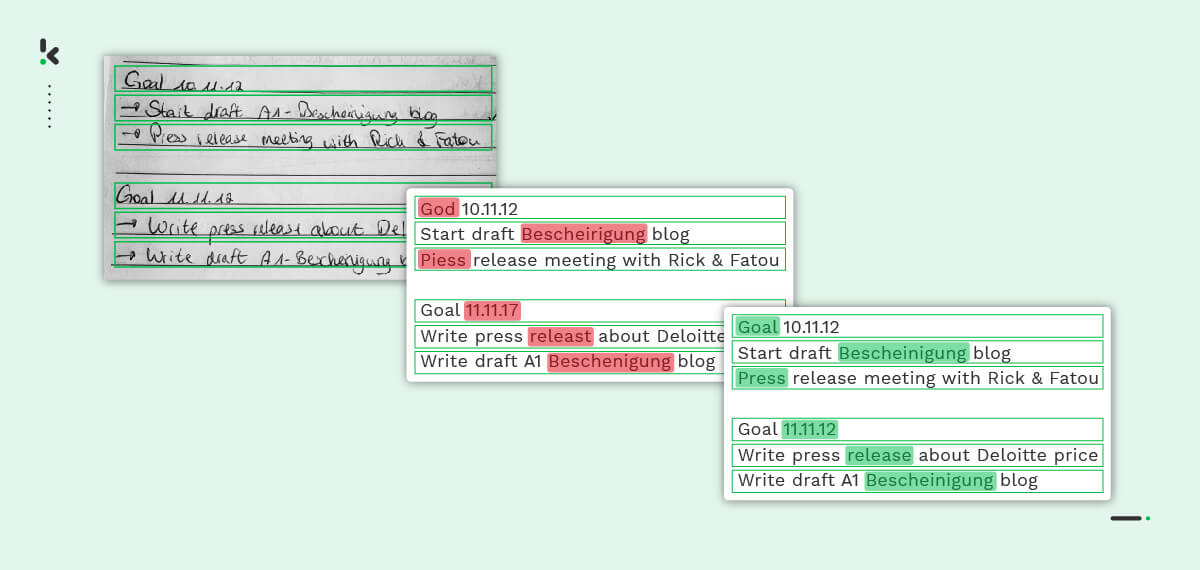

With ICR, businesses can process unstructured data such as handwritten text, and transform it into business-ready data that can be passed on further in their document-related workflows. This of course comes with countless benefits.
Benefits of ICR
Any business that regularly handles a wide range of forms, letters, and papers, such as those in the financial, legal, or healthcare sectors, can benefit from ICR. These benefits include:
- Reduced data entry mistakes – Companies working with large amounts of data can expect an error rate of up to 4%. An ICR solution, with the help of AI and Machine Learning, can help you reduce these errors significantly.
- Lower operational costs – As previously mentioned, manually processing documents can be highly expensive. With ICR you can reduce these costs by up to 90%!
- Shorter processing time – Manual data extraction and verification take 10 to 20 minutes for each document, while ICR can save 70% of that time.
- Scalability – The ICR system is very flexible, enabling it to analyze different types of documents or process vast quantities.
ICR is used by many industries as it is a fast and cheap solution to process large amounts of documents. In the next section of this blog, we’ll take a look at some of its use cases.
ICR use cases
If your business is transitioning to digital workflows but you still need to handle large amounts of paper documents that contain handwriting (such as purchase orders, custom forms, or logistics documents), ICR technology can help you digitize those files.
Intelligent Character Recognition is beneficial in a variety of scenarios. Some of the most popular ICR use cases are listed below (the list is not exhaustive):
- Automate Accounts Payable processes
- Convert Image to Text
- Automate Data Entry
- Extract information from a PDF
- Automate Forms processes
As you can see, ICR has many applications that can empower your workforce, amplify efficiency, and improve data accuracy.
Don’t worry if your use case isn’t listed because there’s a good possibility that Klippa can assist you with a refined ICR solution to automate your document-related workflows.
Why choose Klippa ICR?
If we sparked your interest in ICR software, you don’t have to look any further as we present you Klippa DocHorizon. This Intelligent Document processing solution brings together the best of both ICR and OCR technologies.
With Klippa DocHorizon, you can extract data from both unstructured and structured documents including handwritten signatures or numerical values thanks to AI and Machine Learning. Unlike traditional OCR, DocHorizon does not require the use of templates and is sophisticated enough to continuously learn and interpret data accurately.
Next to data extraction automation, you can automate the following tasks that are often traditionally completed by people:
- Document Classification – Document recognition for easy document archiving
- Document Conversion – Convert unstructured and structured documents into machine-readable format (JSON, CSV, XML, XSLS)
- Anonymization – Mask sensitive data to comply with GDPR regulations
- Data Verification – Verify data with 3rd party databases
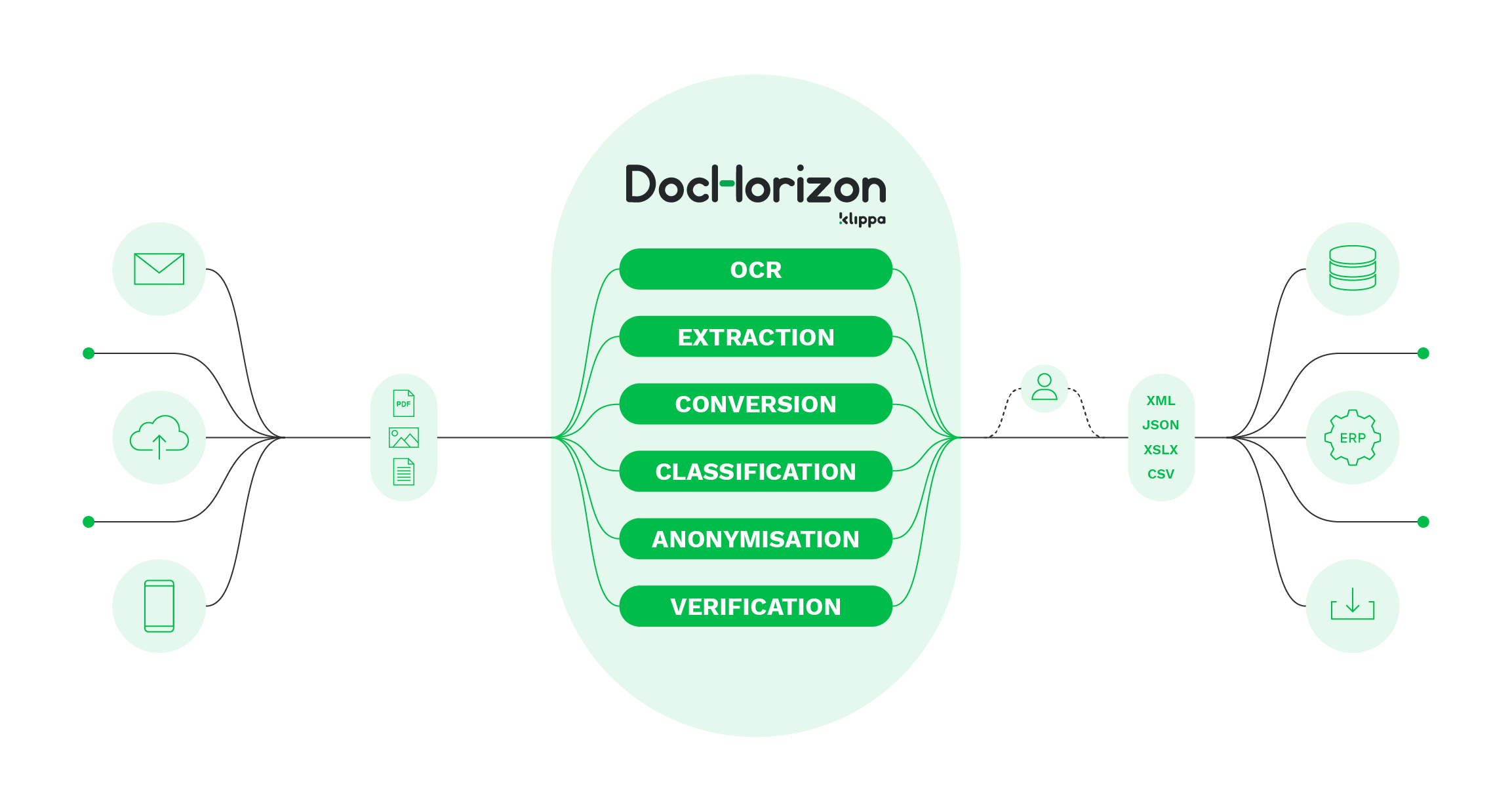

With these features, DocHorizon is the best solution to help you digitize documents within seconds, enhance accuracy, reduce manual entry mistakes, eliminate fraud and empower customer experience.
Curious to know more about our solution? You can simply schedule a demo below or get in touch with us if you have any questions.